Understanding Water Storage Tanks: Essential Insights for Informed Choices
Introduction to Water Storage Tanks
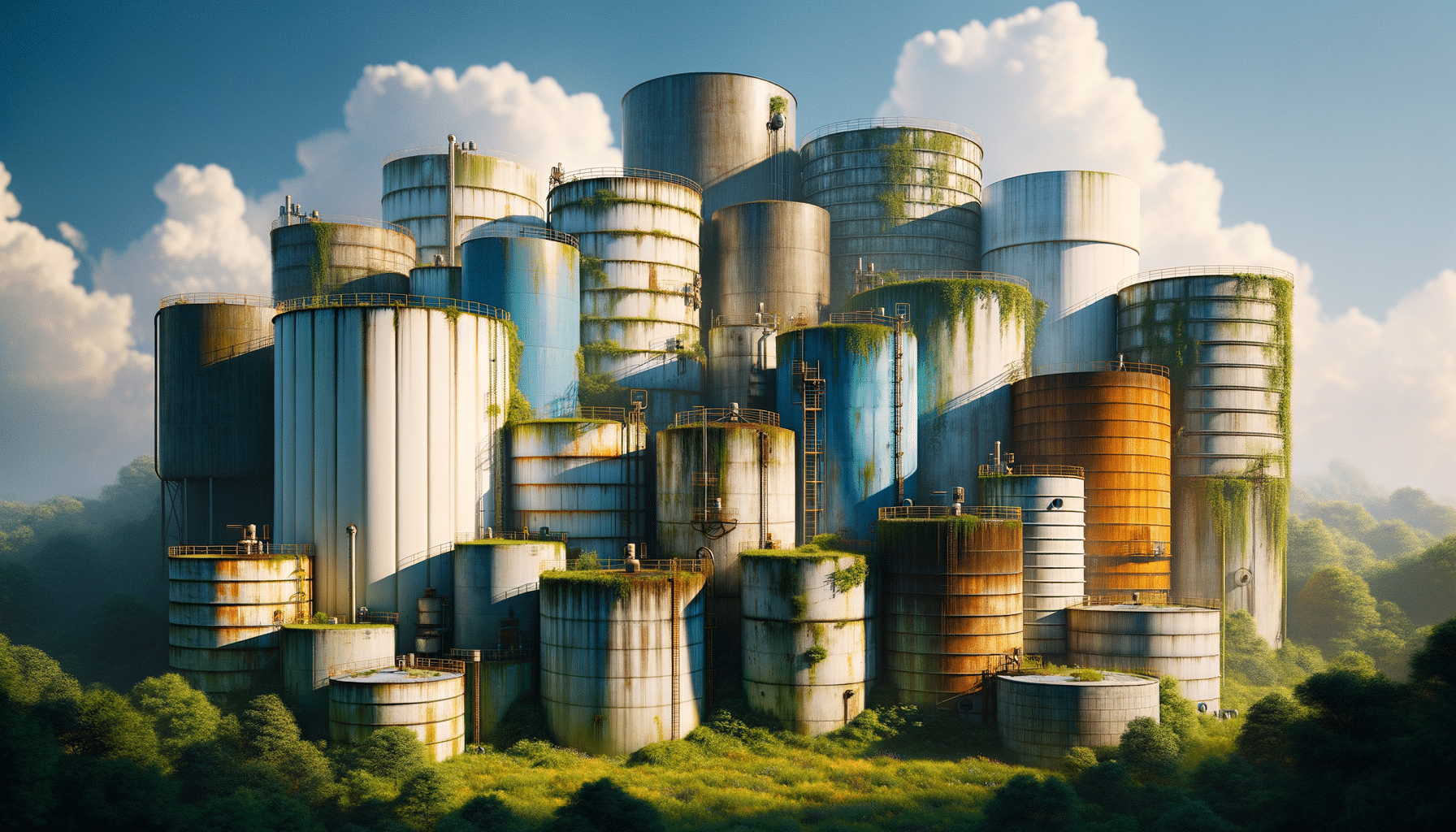
Water storage tanks are an essential component in managing water supply, ensuring access to water in both residential and industrial settings. These tanks are used to store water for various purposes, including drinking, irrigation, fire suppression, and industrial processes. Understanding the different types of water storage tanks, their materials, and their functionalities can help individuals and businesses make informed decisions tailored to their needs.
Water storage tanks serve a critical role in areas where water supply is inconsistent or where there is a need to store large volumes of water. They can vary greatly in size, material, and design, each suited to specific applications and environments. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of water storage tanks, providing comprehensive insights into their importance and functionality.
Types of Water Storage Tanks
Water storage tanks come in several types, each designed to meet specific requirements. The most common types include:
- Plastic Tanks: Made from polyethylene, these tanks are lightweight and resistant to rust and corrosion, making them suitable for residential use.
- Steel Tanks: Known for their durability, steel tanks are often used in industrial settings and can be coated to prevent rust.
- Concrete Tanks: Typically used for underground storage, these tanks are robust and can hold large volumes of water.
- Fiberglass Tanks: Resistant to corrosion and chemical damage, fiberglass tanks are ideal for storing water in harsh environments.
Each type of tank offers unique advantages depending on the intended use. For example, plastic tanks are highly rated for domestic applications due to their affordability and ease of installation. In contrast, steel tanks are renowned for their strength and longevity, making them a preferred choice in industrial settings.
Materials and Construction
The materials used in constructing water storage tanks significantly impact their performance and longevity. Common materials include plastic, steel, concrete, and fiberglass, each offering distinct properties.
Plastic: Plastic tanks, particularly those made from polyethylene, are popular due to their lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion. They are suitable for above-ground applications and are often used for rainwater harvesting systems.
Steel: Steel tanks offer exceptional durability and are often galvanized or coated to prevent rust. They are among the top options for industrial applications due to their ability to withstand high pressures and extreme temperatures.
Concrete: Known for their strength, concrete tanks are ideal for underground installations. They can store vast amounts of water and are resistant to environmental damage.
Fiberglass: These tanks are excellent for environments with harsh chemical exposure. They are lightweight and offer outstanding resistance to corrosion.
Applications and Benefits
Water storage tanks are used in a variety of applications, each providing specific benefits. Some common uses include:
- Residential Use: Tanks are used for rainwater harvesting and emergency water storage, ensuring a reliable water supply during shortages.
- Agricultural Use: Farmers use storage tanks for irrigation, reducing dependency on inconsistent rainfall.
- Industrial Use: Industries use tanks to store water for manufacturing processes or fire suppression systems.
- Municipal Use: Cities use large tanks to ensure a consistent water supply for public distribution systems.
The benefits of water storage tanks include improved water management, cost savings from reduced water bills, and increased preparedness for emergencies. In agricultural settings, tanks can enhance yield by providing a steady water supply, while in urban areas, they contribute to efficient water distribution.
Choosing the Right Water Storage Tank
When selecting a water storage tank, several factors must be considered to ensure it meets the specific needs of the user.
Capacity: Determine the volume of water needed based on usage patterns and ensure the tank can accommodate that amount.
Location: Consider whether the tank will be placed above or below ground and choose materials suited to the environment.
Budget: While plastic tanks are cost-effective, steel and concrete tanks may offer better long-term value due to their durability.
Compliance: Ensure the tank meets local regulations and standards for water storage.
By evaluating these factors, users can select a well-regarded tank that provides exceptional quality and meets their water storage needs efficiently.
Conclusion: Making Informed Water Storage Decisions
Understanding the different types of water storage tanks and their applications is crucial for making informed decisions that align with specific needs. Whether for residential, agricultural, or industrial purposes, selecting the appropriate tank can enhance water management, ensure reliable access, and provide significant economic benefits. By considering factors such as material, capacity, and location, users can choose a tank that offers outstanding performance and longevity.